Binomial and Normal Distribution
>二項分佈(binomial distribution)
A binomial distribution can be thought of as simply the probability of 2 outcomes in an experiment or survey that is repeated multiple times.
For example, a coin toss has only two possible outcomes: heads or tails and taking a test could have two possible outcomes: pass or fail.
A Binomial Distribution shows either (S)uccess or (F)ailure.
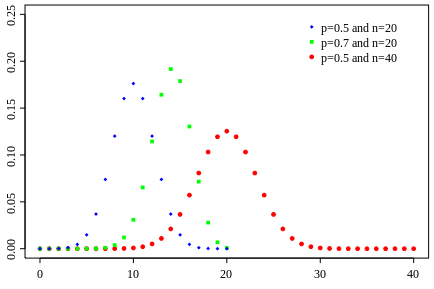
The first variable in the binomial formula, n, stands for the number of times the experiment runs. The second variable, p, represents the probability of one specific outcome.
橫軸是試驗結果中成功/失敗的次數, 縱軸是該結果的機率.
If X ~ B(n, p), that is, X is a binomially distributed random variable, n being the total number of experiments and p the probability of each experiment yielding a successful result, then the expected value of X is
E[X] = np
Var(X) = np(1-p)
常態分佈(normal distribution)



留言