Physical Layer
網路接頭壓剝剪鉗
Difference Between RJ11 and RJ12
The registered jack standard has been around for some time for people to follow in wiring their telephone lines. It is abbreviated into RJ and is then followed by two digits that identify the specific standard.
Both RJ11 and RJ12 wiring standards are used for the same purpose, telephone lines.
Both RJ11 and RJ12 use the same six slot connector.
The only difference between these two is in how they are wired and the number of the wires that are being used.
- RJ12 is a 6P6C wiring standard. This means that there are also 6 wires that are terminated in the connector, occupying all the available slots.
- RJ11 is a 6P4C wiring standard Only four wires connected and the remaining two slots are no longer used.
一般與跳線的使用上有何不同?
- 一般接線使用於電腦透過HUB連接。 一端接在電腦上,另一端則必須接再HUB等設備上,不可與其他電腦直接對接。 一般網路線與網路頭的接線順序為:
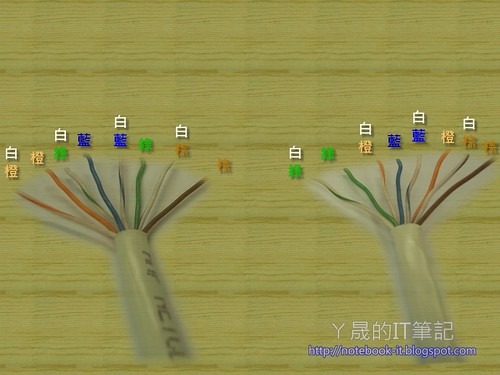
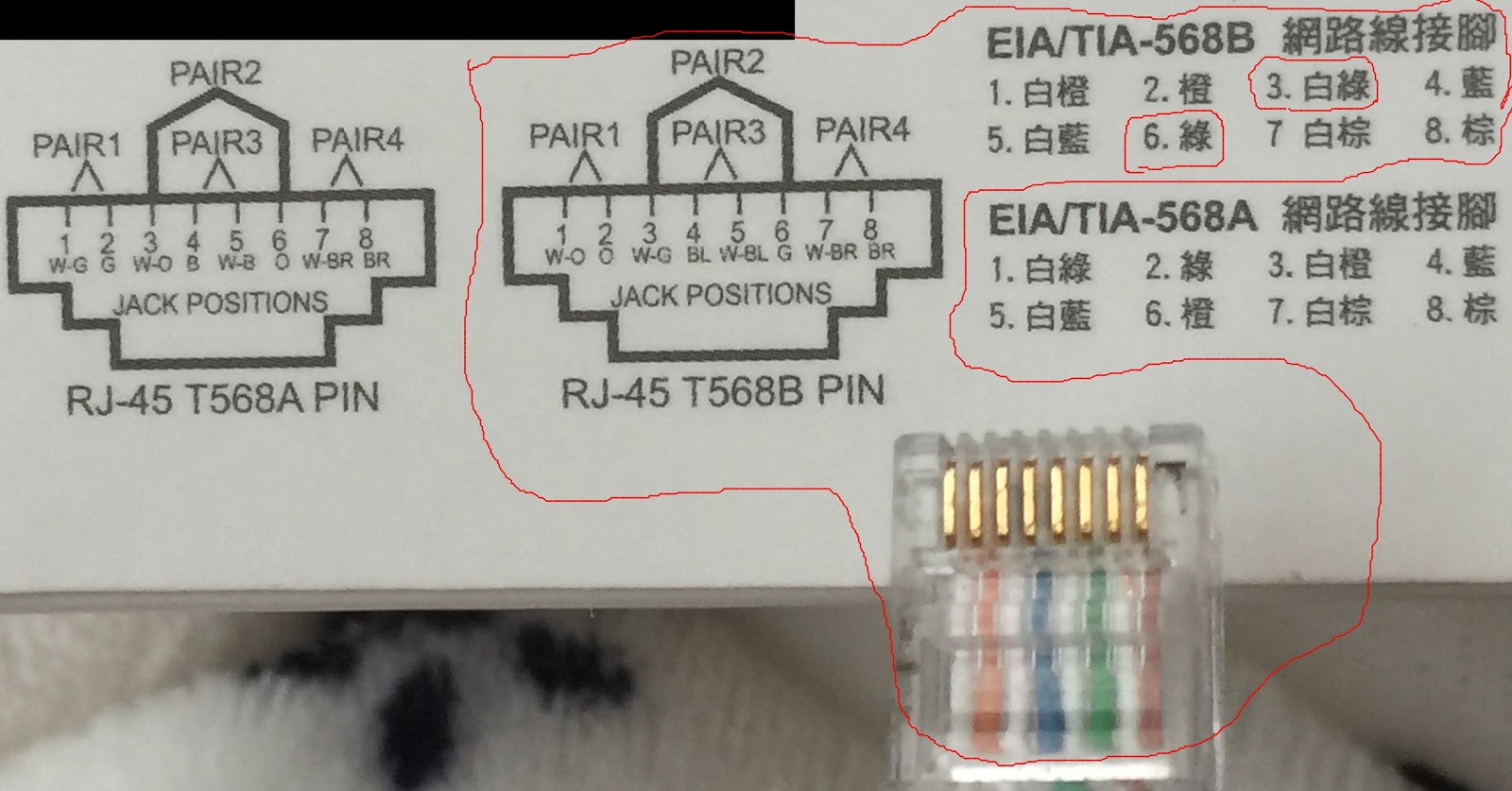
A端:白橙、橙、白綠、藍、白藍、綠、白棕、棕 B端:白橙、橙、白綠、藍、白藍、綠、白棕、棕也就是說,A、B兩端的順序是相同的。
A端:白橙、橙、白綠、藍、白藍、綠、白棕、棕 B端:白綠、綠、白橙、藍、白藍、橙、白棕、棕也就是把『橙色組』線與『綠色組』順序對調。
【PowerSync 群加】網路接頭壓剝剪鉗(HT-5468R)
功能:剝線剪線壓接
- 用於壓接8P8C/RJ45, 6P6C/RJ12, 6P4C4P4C/RJ11水晶頭
- 適用於網路與電話接頭
- 附棘輪和Release裝置,壓著省力,不卡死
- 附剝線功能,可剝網路線外
- 附剪線功能(反面),可更換刀片
【群加 Powersync】CAT 5e RJ45 8P8C 網路水晶接頭 / 50入(CAT5E-G8P8C350)
自己動手 DIY RJ45 網路線接頭吧!
- 用斜口鉗在大約留三公分長度的部份用前端部份慢慢將外皮給剪斷一圈
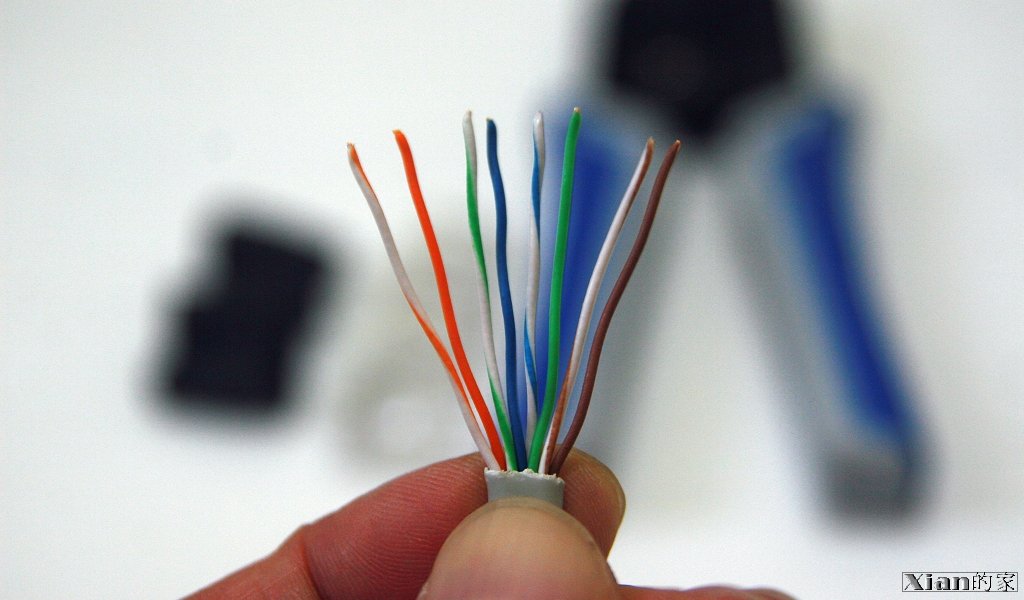
- 內線分四對:分別為"橘白+橘","綠白+綠","藍白+藍","棕白+棕"
- 將該每對對絞線分開由左到右為:橘白、橘、綠白、綠、藍白、藍,棕白、棕
- 將每條線給整直.綠線與藍線對調位置成由左到右為:橘白、橘、綠白、藍、藍白、綠,棕白、棕
- 用壓線鉗剪線端將剛剛留的三公分長度的線剪齊剪短剩大約1.3公分
- 固定彈片向外,另一面向自己,將線給插進去網路接頭內 將線用力往裡面塞,塞到底,然後注意檢查每條線的位置是否正確。
- 檢查2邊的線有無插到底。
- 8P是網路線,將剛剛的網路接頭塞進8P的位置,要塞到底
- 用雙手用力把壓線鉗壓到底,一定要壓到底不要怕壓壞,壓到底放開再壓一次到底即可!
Key Operations
- 用在戶外時, 須買"工程級"的網路線
- Make sure the lines is in order
- Make sure the metal contacts are all pushed in
- 不要一次就施全力壓 鉗子有可能在重壓時偏離接觸點, 會把接觸點壓偏
- 一次壓一點
- 確定鉗子可以正確接觸到金屬片時再輕壓
- 看到金屬片都能被壓下時, 再施全力壓
‧UTP 網路線:為八股對絞單芯線,無遮蔽 ‧FTP 網路線:為八股對絞單芯線,鋁箔遮蔽 ‧SFTP (簡稱STP)網路線:為八股對絞單芯線,鋁箔+銅編織網遮蔽 ‧Cat.5 100MHz 工作頻率 ‧Cat.5e 100MHz 工作頻率(為Cat.5加強型最大可到 350MHz 但無認證標準) ‧Cat.6 1GHz 工作頻率(為十字對絞線,每對工作頻率 250MHz 共四對) ‧Cat.5 - 100MHz / Cat.5e - 125MHz / Cat.6 -1Giga電腦網路 電纜線
MDI vs MDIX And Auto MDI/MDIX Basics
MDI/MDIX are types of Ethernet interface (both physical and electrical/optical) in a computer network used to carry transmission. They must be connected using the right twisted pair cable so that the transmission pair on one end is linked to the receiving pair on the other end, and vice versa.MDI vs MDIX: What Is the Difference?
MDI (Medium dependent interface), also known as an uplink port, is an Ethernet port connection typically used on the NIC (Network Interface Card) or Integrated NIC port on a PC. The transmission signals on a NIC must go to receiving signals on the hub or network switch, so the latter devices have their transmission and receiving signals switched in a configuration known as MDIX – the “X” here represents “crossover”, indicating the reverse of input and output signals. MDIX (Medium Dependent Interface Crossover) is an 8P8C port connection often found on a computer, router, hub, or network switch. Since MDIX is the crossover version of the MDI port, the pins 1 and 2 (transmitting) on an MDI device go to pins 1 and 2 (receiving) on an MDIX device via a straight through cable. Similarly, pins 3 and 6 (receiving) on an MDI device go to pins 3 and 6 (transmitting) on an MDIX device. In this case, the MDIX port eliminates the need for a crossover twisted pair cabling.
What About Ethernet Auto-MDI/MDIX?
As aforementioned, an Ethernet crossover cable is adopted to connect two ports of the same configuration (i.e. MDI-to-MDI or MDIX-to-MDIX). However, it may generate some confusion and inconveniences when deploying two different kinds of Ethernet cables. The auto-MDI/MDIX technology is developed to fix this problem: It automatically switches between MDI and MDIX as required.Auto MDI/MDIX ports on newer device interfaces detect if the connection requires a crossover, then automatically choose the MDI or MDIX configuration to properly match the other end of the link. In this case, it doesn’t matter if you using straight through or crossover cables. The chart below shows cable types for MDI/MDIX and auto-MDIX.
Ethernet(以太網)之 詳解 MAC、MII、PHY
在實際的設計中,以上三部分並不一定獨立分開的。通常,將MAC集成進微控制器而將PHY留在片外。 更靈活、密度更高的芯片技術已經可以實現MAC和PHY的單芯片整合。 比較常見:CPU不集成MAC與PHY,MAC與PHY採用集成芯片。 MAC及PHY工作在OSI七層模型:






























留言